Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R Gen 3 (2008-2010) Maintenance Schedule and Service Intervals
This is the maintenance schedule with associated service intervals for the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R Gen 3, made between 2008-2010. It’s also sometimes written “ZX10R”.
The 3rd gen Kawasaki ZX-10R was a welcome evolution after the Gen 1 and Gen 2 Ninja ZX-10R, which shared an engine base. Fans always liked the engine, but the handling was questionable, and this translated into not as good racing results and sales performance as the other market leaders.
From 2008, Kawasaki made a host of changes, including giving it a more rigid frame, improving the ergonomics so the rider has more “rider feel”, improved suspension, and improved braking. Engine performance was significantly improved too, putting out a huge 140-150 kW (188-200 hp) at the crank — going up with the assistance of ram air.
From 2011, Kawasaki released the Gen 4 Kawasaki ZX-10R, which brought with it electronics.
This site has links for things like oil and spark plugs from which we earn a commission (which unfortunately nobody can save, not even us). If you appreciate this work, then please use those links. Thanks!
Kawasaki ZX-10R Service Intervals (3rd gen)
The 3rd gen Kawasaki ZX-10R has 7500 mile / 12000 km or annual service intervals. At every service, change the oil and filter, and do a host of checks.
The manual specifies a shorter service interval, but the only checks required there are on brakes and emissions equipment. As a rider will check brakes more often than that, it seems redundant to include that much detail.
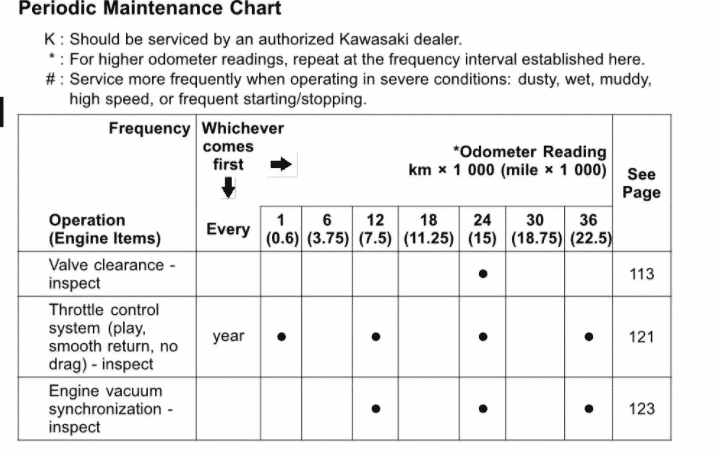
The main valve service interval is every 15000 miles or 24000 km.
Aside from that, regularly maintain the chain, and replace the brake and clutch fluid.
Kawasaki ZX-10R Generations
Before you ask “Why is this a such-and-such ZX-10R”, here are the generations of the ZX-10R, according to obsessive forum people, and also Wikipedia.
- Kawasaki ZX-10R Gen 1 (C1-C2, 2004-2005): Dry weight 170kg, 130 kW (175 hp) @ 11,700 rpm. Brakes are 300mm dual radial-mounted discs with four-piston calipers.
- Kawasaki ZX-10R Gen 2 (D1-D2, 2006-2007): Dry weight 174 kg, power 130 kW (175 hp) @ 11,700 rpm. A make-over that smoothed out the Gen 1 (with otherwise the same engine) with different injectors, heavier flywheel, and an under-seat exhaust. The “least desirable” ZX-10R per forums. Same brakes as Gen 1.
- Kawasaki ZX-10R Gen 3 (2008-2010): Dry weight 179 kg, 140-150 kW (188-200 hp) @ 12,500 rpm, going up with ram air. Longer wheelbase, extended rake, black fork tubes, Öhlins steering damper, adn new bodywork. Brakes upgraded to 310mm petal discs
- Kawasaki ZX-10R Gen 4 (2011-2015): Dry weight 187 kg, 150 kW (200 hp) @ 13,000 rpm (with ram air). Revised porting, higher lift cams, and higher compression. New twin-spar frame with horizontally-mounted shock. KTRC traction control, power modes, and optional ABS (a rarity on superbikes at the time). Big Piston fork suspension, replacing regular inverted forks. Same brakes as Gen 3.
- Kawasaki ZX-10R Gen 5 (2016-2020): 148 kW (197 hp) with ram air @ 13,000 rpm. An IMU giving lean angle-aware ABS and traction control. Launch control mode, quickshifter, and engine brake control. Also slipper clutch, and lighter engine components. Less restrictive air filter and exhaust. Brakes are 330mm circular discs with Brembo M50 monoblock calipers. Balance Free Fork suspension.
- Kawasaki ZX-10R Gen 6 (2021+): 150 kW / 204 hp @ 14000 rpm, or 157.5 kW / 214 hp with ram air. Higher power through a high-speed valvetrain, more aggressive cam profile, air-cooled oil cooler, electronic throttle valves and valve train (allowing the bike to rev higher), gearbox ratios changed for shorter gears 1-3, electronic cruise control, TFT display, Bluetooth connectivity, integrated winglets and a more aerodynamic front cowl (more downforce, less drag), LED headlights and tail-lights
Maintenance Schedule for the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R Gen 3
Below is the maintenance schedule for the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R Gen 3, combined into one super-table.
Notes:
- For higher odometer readings, repeat at the frequency interval established here.
- Follow the earlier of time-based or distance-based service intervals
- Kawasaki recommends items relating to emissions or safety be serviced by an authorised dealer.
- Service the oil, chain, air cleaner, and brakes more often if riding in dusty, wet, muddy, or aggressive riding conditions.
- The manual recommends you check the brake system and steering damper more regularly (between services)
| mi x 1000 | 7.5 | 15 | 22.5 | 30 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km x 1000 | Every | 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 |
| Engine oil – change | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Oil filter – replace | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Air cleaner element – replace | 11250 mi / 18000 km | ||||
| Fuel hoses – replace | 4 years | ✓ | |||
| Coolant – change | 3 years | ✓ | |||
| Radiator hoses and O-rings – replace | 3 years | ✓ | |||
| Brake hoses – replace | 4 years | ✓ | |||
| Brake fluid (front and rear) – change | 2 years | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Rubber parts of brake master cylinders and calipers – replace | 4 years | ✓ | |||
| Spark plug – replace | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
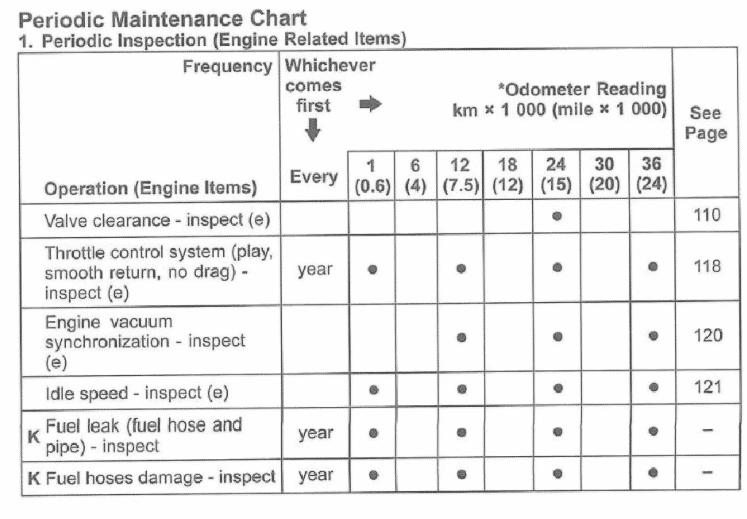
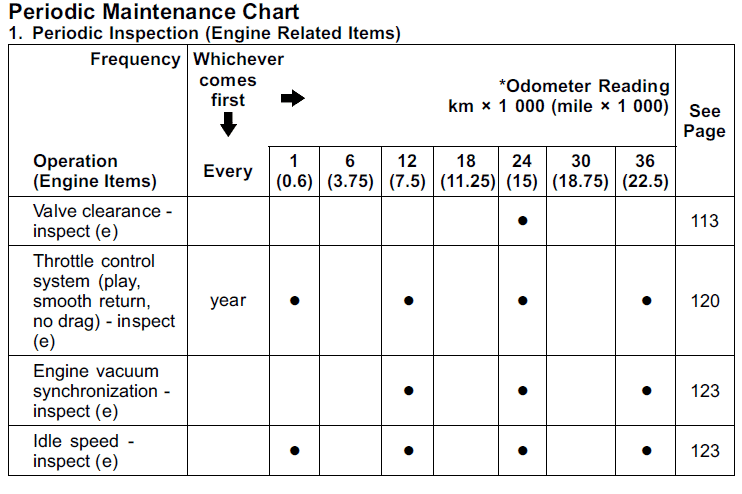
| Valve clearance – inspect | ✓ | ||||
| Throttle control system (play, smooth return, no drag) – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Engine vacuum synchronization – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Idle speed – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Fuel leak (fuel hose and pipe) – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Fuel hoses damage – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Fuel hoses installation condition – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Coolant level – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Coolant leak – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Radiator hose damage – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Radiator hoses installation condition – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Evaporative emission control system – function (if installed) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Air suction system damage – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Clutch operation (play, engagement, disengagement) – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Drive chain wear – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Drive chain guide wear – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Wheels and tires: | |||||
| Tire air pressure – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Wheels/tires damage – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Tire tread wear, abnormal wear – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Wheel bearings damage – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Brake system: | |||||
| Brake fluid leak – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Brake hoses damage – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Brake pad wear – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Brake hose installation condition – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Brake fluid level – inspect | 6 months | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Brake operation (effectiveness, play, drag) – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Brake light switch operation – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Suspensions: | |||||
| Front forks/rear shock absorber operation (damping and smooth stroke) – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Front forks/rear shock absorber oil leak – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Uni-trak rocker arm operation – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Uni-trak tie rods operation – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Steering System: | |||||
| Steering play – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Steering stem bearings – lubricate | 2 years | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Steering damper oil leak – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Electrical System: | |||||
| Lights and switches operation – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Headlight aiming – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Side stand switch operation – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Engine stop switch operation – inspect | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Chassis: | |||||
| Chassis parts – lubricate | year | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Bolts and nuts tightness – inspect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Maintaining Your Chain on the Kawasaki ZX-10R
It’s important to maintain your chain on the ZX-10R, as on any chain-driven motorcycle. Use a good-quality chain lubricant like Motul chain paste, or a Motul chain care kit which comes with a couple of handy tools to maintain the chain.
Kawasaki recommends you follow the following chain maintenance schedule:
| Chain maintenance item | Every |
|---|---|
| Check drive chain lubrication condition, lubricating if necessary (Motul chain paste) | 400 mi / 600 km |
| Check drive chain slack, adjusting if necessary | 600 mi / 1000 km |
Notes:
- Do these items (checking/adjusting slack, and checking/applying lubrication) more often if you ride your ZX-10R in dusty or rainy conditions.
- Always lubricate the chain after washing the motorcycle.
Tyre size and tyre pressure for the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R Gen 3
The Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R Gen 3 has the following tyres and tyre sizes standard:
| Wheel | Size | Brand(s) | Tyre pressure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Front | 120/70 ZR17 M/C (58W) | PIRELLI “DIABLO CORSA III N” BRIDGESTONE “BATTLAX BT016F J” | 250 kPa/36psi |
| Rear | 190/55 ZR17 M/C (75W) | PIRELLI “DIABLO CORSA III” BRIDGESTONE “BATTLAX BT016R J” | 290 kPa/42psi |
About the 2008-2010 Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R Gen 3
The 2008-2010 3rd gen Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R is the first model that (aside from those trying to collect them all) catches the eyes of many people looking for a classic ZX, mostly because it was more powerful AND handled a lot better than previous generations.
The Gen 3 Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R still looks new, and it is all due to the now more svelte bodywork, which you’ll most likely notice that it perfectly resembles that of the bike’s smaller sibling, the ZX-6R (which always looks good). The new look is complemented by the blacked-out exhaust.
The engine is the same 998cc, liquid-cooled, inline-four, DOHC with four valves per cylinder, but with the help of a lot of revised internals, has been improved to produce a peak of 150 kW (200hp) with ram air.
The 2008-2010 ZX-10R has an early form of power control called KIMS (“Kawasaki Ignition Management System”). This was designed to keep “unwanted” throttle under control. KIMS worked by monitoring engine speed, throttle position, gear position, intake air pressure, and temperature, to determine sudden spikes in engine speed. If they happened, then ignition would be retarded.
The KIMS system only works in neutral or closed throttle applications, like if you hit a patch of gravel. It’s not traction control because it doesn’t rely on wheel speed sensors.
The 2008 has a big, easy-to-read analogue tachometer that’s a pleasure to follow when as it climbs towards the 13,000 rpm redline. The LED display inside the tacho shows the speed, gear, and has a lap timer, too.
The improvements to the suspension for the ZX-10R are difficult to explain, but owners say that the 2008-2010 ZX-10R “talks” to the rider a lot more. You’re a lot more in contact with the bike, and the suspension and chassis communicate the ride to you more effectively.
Pretty much the only complaint about the 2008-2010 ZX-10R is that its foot-pegs touch down a bit sooner than you’d expect if you’re the kind of rider who gets into full lean regularly. Most riders probably won’t notice. Aftermarket rear sets help.
Kawasaki’s strategy was to maintain building costs at a minimum and so be able to price the new-for-2008 ZX-10R at US$13K, which was very impressive, and helped its popularity to soar.
The 2011 Ninja ZX-10R, with its host of rider aids, was an obvious improvement, but the 2008-2010 is the favoured gen for people who don’t want their bike saddled with tech.
Reference — Manual for the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R Gen 3
The above maintenance schedule comes directly from the user’s manual for the 2010 Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R, which is available at Kawasaki’s website here. You can see from the screenshots above that it’s the same maintenance schedule as for the other years of the same generation ZX-10R.